The National Fusion Laboratory is a department of CIEMAT, where its operations commenced in 1998. The research carried out at the laboratory is divided into two main groups:
- the study of high-temperature confined plasmas, and
- the research and development of technologies and materials needed to build and operate future fusion reactors.
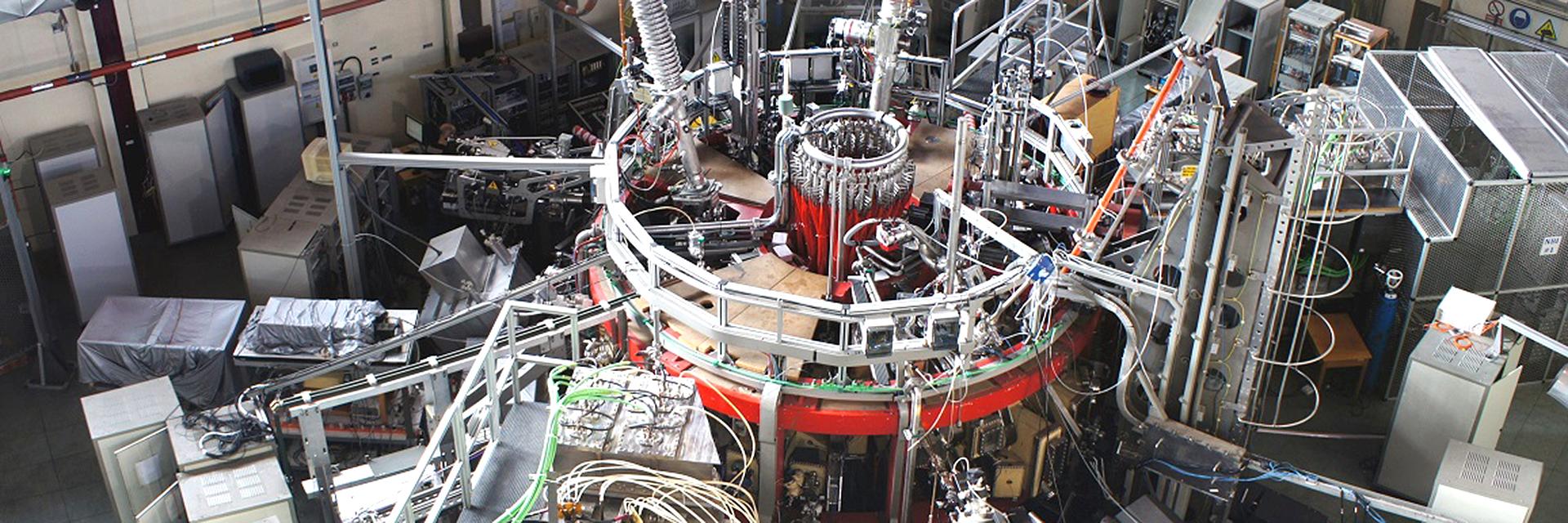
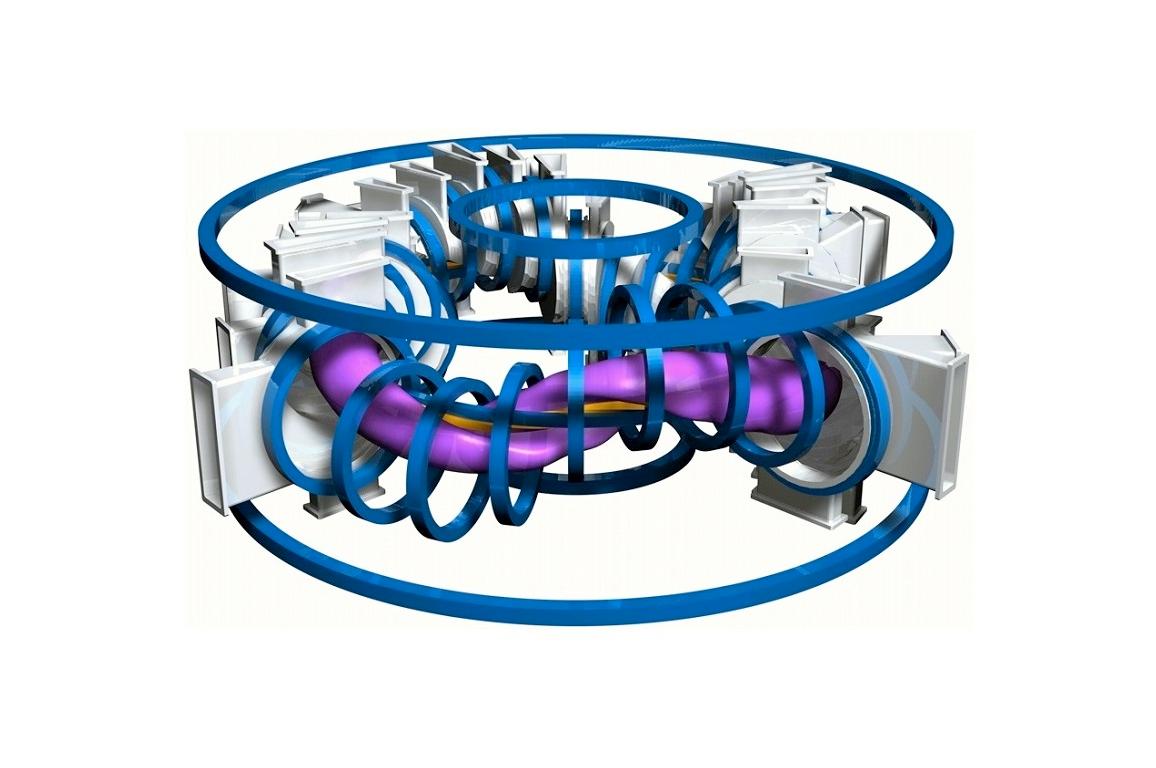
The main component of this laboratory is the TJ-II, a stellarator-type magnetic confinement device. This toroidal-shaped fusion reactor has a minor radius of 0.2 m, a major radius of 1.5 m and a magnetic field of 1 Tesla. In terms of size, it is a medium-sized stellarator.
It reaches extremely high temperatures in its interior by applying 800 kW of radiofrequency (53 GHz) and 1.6 MW of neutral hydrogen injection accelerated to 49 keV.
In addition, there are 92 access windows for the installation of measurement systems used in different experiments.
The laboratory is also equipped with instruments for material modification using radiation and facilities for the characterisation of the chemical, physical, and mechanical properties of materials for use in nuclear fusion processes.