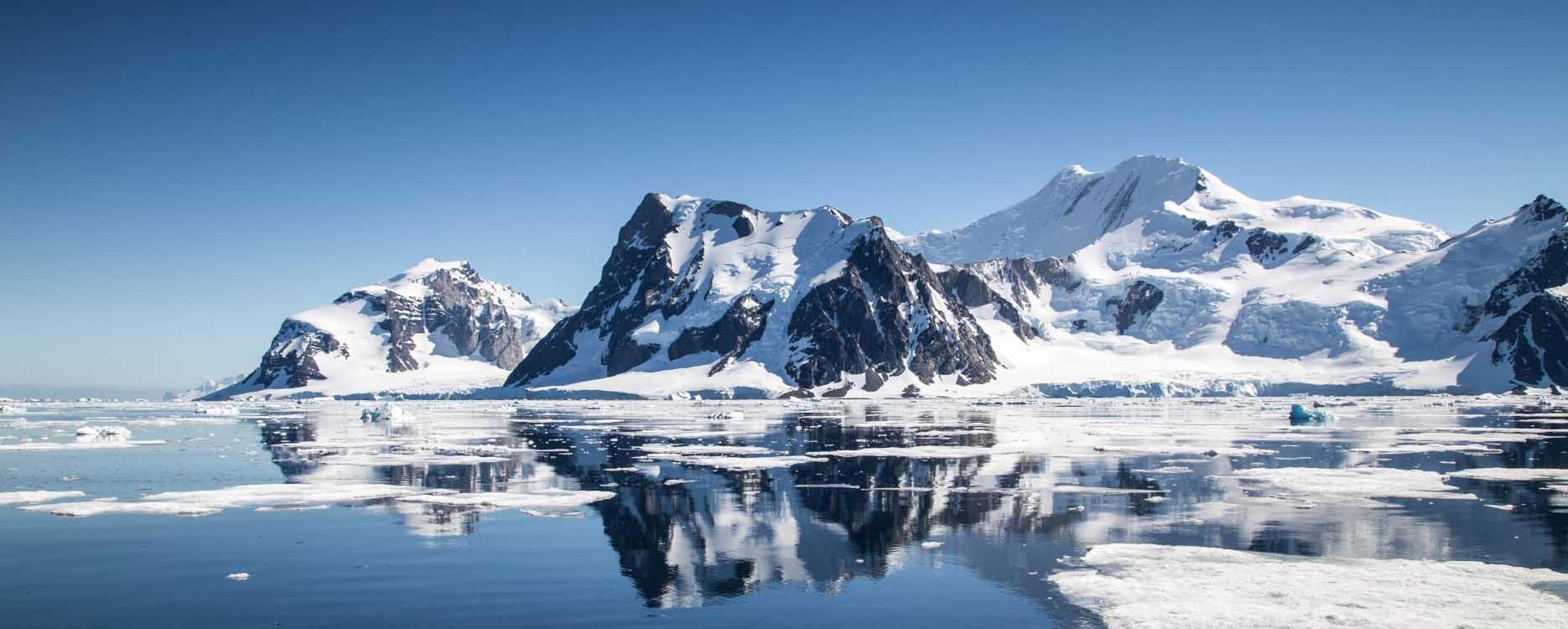
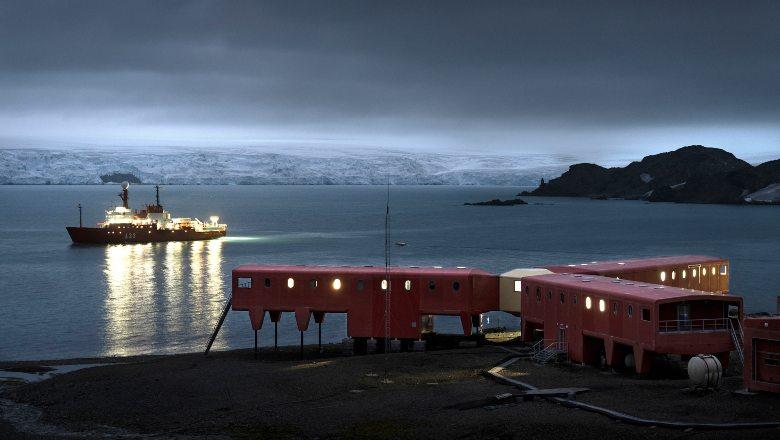
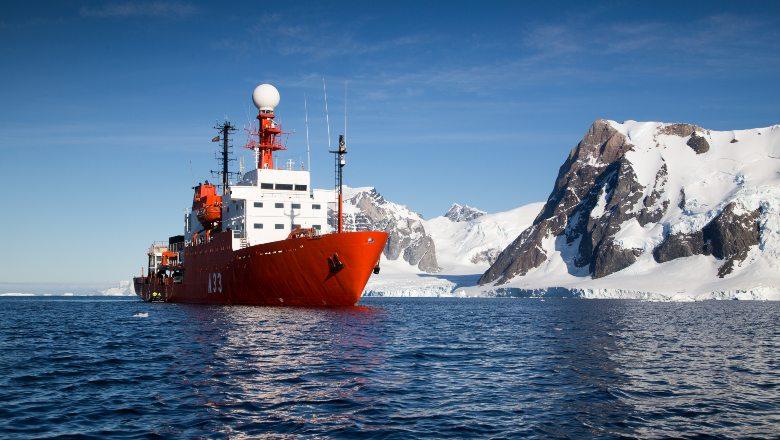
The Spanish Polar Committee (CPE) is the Spanish authority responsible for coordinating Spain's R&D&I activities in the polar regions. Royal Decree 852/2020 of 22 September regulates its composition and operation.
The CPE is currently assigned to the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities through the General Secretariat for Research, which holds the Committee Chair as the National Polar Authority. In addition, the CPE is made up of a series of members represented by the different ministries and institutions involved in Spain's polar activity; and a Technical Secretariat, which is responsible for promoting, coordinating and overseeing the activities determined by the Committee or those assigned to it by the National Polar Authority.