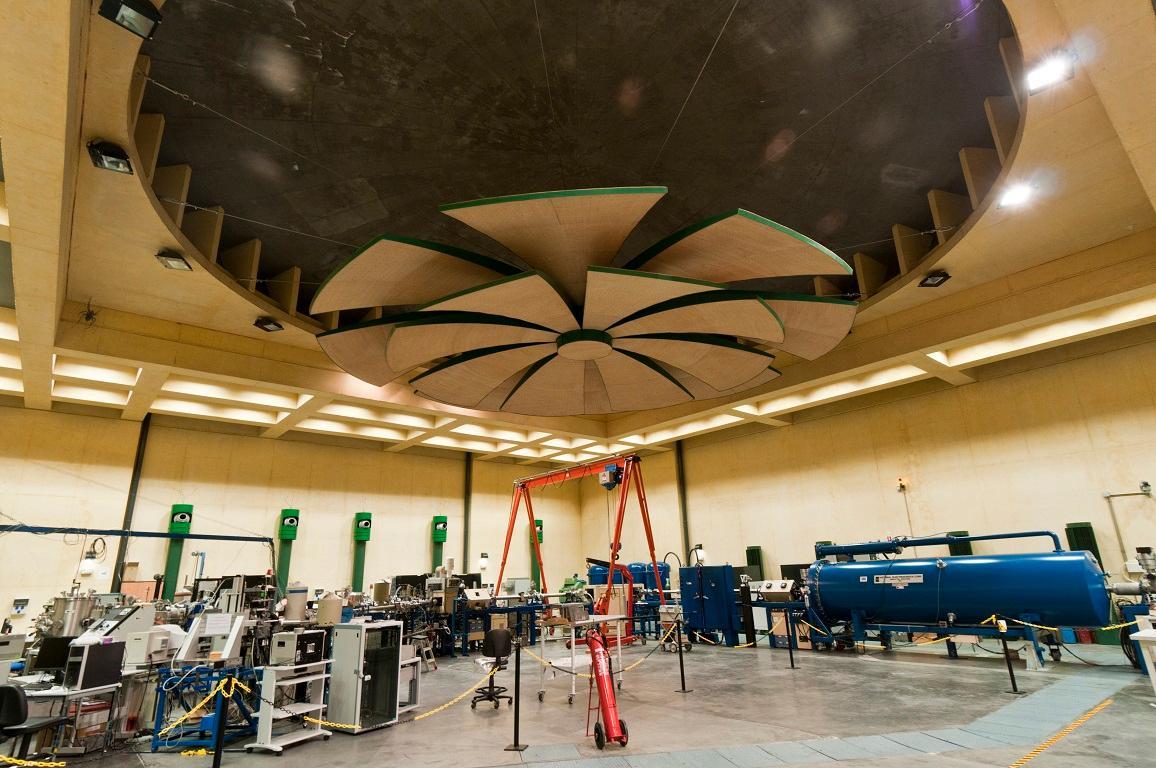
This distributed ICTS consists of two infrastructures: the National Accelerator Centre (CNA) and the Centre for Microanalysis of Materials (CMAM).
National Accelerator Centre (CNA)
The National Accelerator Centre is a joint centre operated by the University of Seville, the Regional Government of Andalusia and the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC). It is located in a dedicated building in the Isla de la Cartuja Technology Park in Seville.
The CNA has four accelerators:
- A 3 MV Van de Graaff Tandem accelerator, which supports a wide range of analytical techniques and is equipped with the only neutron production line (Hispanos line) of its kind in Spain.
- A 1 MV Tandem Cockcroft-Waltron (Tandetron) accelerator for mass spectrometry (determination of high half-life radionuclides present in trace concentrations in various types of samples). It is used to study environmental processes, archaeology and palaeoanthropology.
- A Micadas mass spectrometer accelerator, specifically developed to determine and measure C-14. It provides an associated C-14 dating service and is used for various forensic studies.
- A cyclotron, supplying 18 MeV protons, used for the production of radiopharmaceuticals and research in physics and nuclear medicine.
The CNA also has other significant instruments and equipment:
- A PET/CT scanner for large animals and humans, which, in conjunction with the cyclotron, makes it possible to study very short-lived radiopharmaceuticals that would otherwise not be feasible.
- A highly versatile 60 Co irradiator capable of performing photon irradiation tests in diverse fields such as aerospace technology, ionising radiation metrology or the irradiation of biological samples for research purposes.
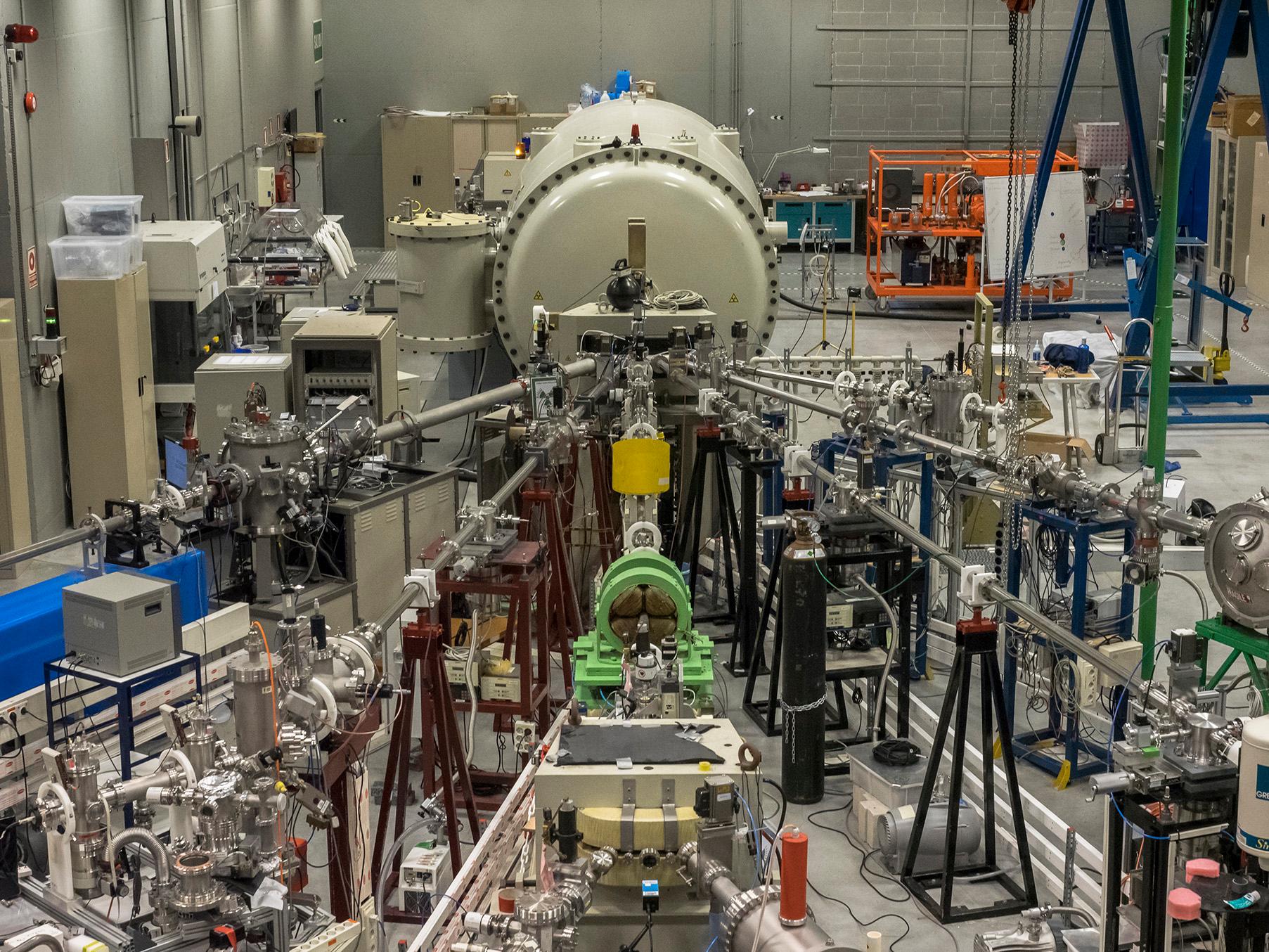
Centre for Microanalysis of Materials (CMAM)
The CMAM is a research centre of the Autonomous University of Madrid (UAM). Its main experimental instrument is an electrostatic particle accelerator with a maximum terminal voltage of 5 MV, dedicated to the analysis and modification of materials. The accelerator is operated through a series of beamlines coupled with various ancillary scientific tools and laboratory support spaces.
The CMAM was founded following an initial project funded through the FEDER programme and originally directed by Professor Fernando Agulló López, assisted by an Advisory Committee made up of prominent members of the Spanish scientific, cultural and academic community.
CMAM operates its accelerator (built by the company HVEE) with six beamlines, which are available to users for materials analysis and modification:
- Standard Multipurpose Line (STD).
- External Microbeam Line (EuB).
- Time-of-Flight Line (ERDA-TOF).
- Nuclear Physics Line (NUC).
- Implantation Line (IMP) and Femtosecond Laser.
- Internal Microbeam Line (IuB).
